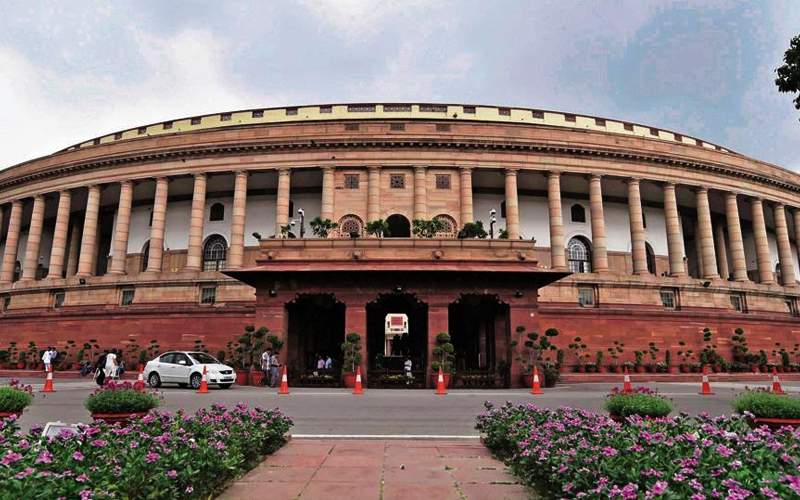
The Citizenship Amendment Bill 2019 has fuelled a lot of protests around the country. The bill was cleared by Lok Sabha on Monday, during the Winter Session by 293 ‘Yes’ and 82 ‘No’. The Opposition and certain NDA leaders from the Northeastern states have stated that this bill is not in the spirit of the Indian Constitution. In response, the Bharatiya Janata Party-led (BJP) government said that the bill is in line with their 2014 general elections’ manifesto. If you’re wondering what the Citizenship Amendment Bill (CAB) is, here’s all you need to know about it.
Background
Citizenship Amendment Bill was first introduced in the Lok Sabha on 19 July 2016. It acts as an amendment to the Citizenship Act, 1955. In early 2019, the bill was passed by Lok Sabha but wasn’t presented in Rajya Sabha. So, as mandated by law, the bill had to be re-introduced in the Lok Sabha.
What does it mean?
Citizenship Amendment Bill states that any illegal immigrant hailing from Afghanistan, Pakistan and Bangladesh will be eligible for Indian citizenship, granted, the person belongs to any of the following communities:-
#1 Hindu
#2 Buddhist
#3 Jain
#4 Parsi
#5 Christian
#6 Sikh
The bill also prevents any of the applicable candidates from being sent to jail or being deported, due to the lack of valid travel documents.
The Citizenship Amendment Bill reduces the number of years, applicants need to spend in India from 11 to 6.
Any illegal immigrant, fulfilling the above criteria, who has resided in India since 31 December 2014, is applicable for Indian citizenship.
Illegal Immigrants without proof of birth can wait for 6 years to apply for Indian citizenship.
Also, the bill contains a provision to cancel Overseas Citizen of India (OCI) registration of any person if the cardholder has violated any Indian law.
As per Citizenship Act 1955, any person who has entered India without valid travel documents like passports and visas or has valid travel documents but has extended his period of stay is an illegal immigrant. The Act required illegal immigrants to be sent to jail or deported back to their home country.
Who is exempted from the Citizenship Amendment Bill?
The states of Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Mizoram, almost the whole of Meghalaya, parts of Assam and Tripura are exempted from the Citizenship Amendment Bill. Manipur is not exempted from this bill.
Why is it being opposed?
The ones protesting the bill claim that it is in violation of Article 14 of the Indian Constitution, which is the “Right to Equality”. Politicians in Assam oppose this bill because it goes against the Assam Accord (1985), which authorised the deportation of all illegal immigrants from Bangladesh to Assam who came during the 1971 Bangladeshi War of Liberation.
While the Citizenship Amendment Bill is yet to come into action, the opinion on it remains divided.









Discussion about this post